Knowledge transfer at the service of the new particle physics strategy
Accelerators, detectors, and computing will pave the way for new discoveries and CERN’s Knowledge Transfer group will be on board to maximise their societal impact.

The expertise of the CERN specialists continues to be an important source of knowledge for the work of the MedAustron experts.
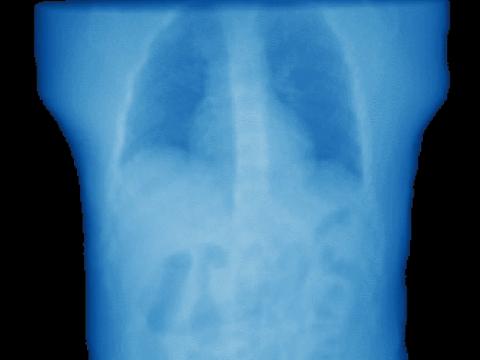
In 2016, CERN and the University of Bath released a new shareware toolbox for fast, accurate 3D X-ray image reconstruction with applications in medical imaging for cancer diagnosis and treatment.

Sharing software and codes in big data environments is a challenge. To do this efficiently researchers at CERN have developed a system called CernVM-FS, for CERN Virtual Machine File System, which is currently used in high-energy physics experiments to distribute about 350 million files.
The Hyperloop competition, intiated by SpaceX and Tesla founder Elon Musk, sets the challenge of devising a pod-like transportation system travelling at sonic or even ultrasonic speeds in high-vacuum tubes over several hundreds of kilometres - reducing travel times from hours to minutes.
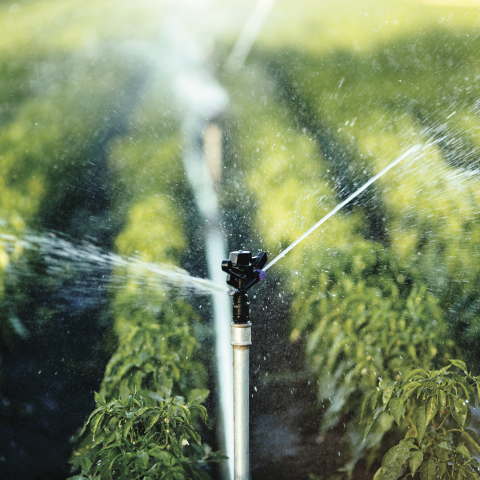

Since 2016, CERN is part of a research project to develop a system for optimised irrigation, based on technologies developed for high-energy physics.

The CERN Robotics Software is used to manage autonomous movement, which allows a modular robotics platform to perform sophisticated tasks.

CERN technician Didier Lombard developed a compact new pipe-cutting tool for the Large Hadron Collider, with potential applications in the gas and petrol industry.

The National Center for Oncological Hadrontherapy (CNAO) in Pavia, Italy, is a facility offering advanced therapy to fight cancer and one of only five centres in the world treating with both protons and carbon ions.

CERN-MEDICIS (Medical Isotopes Collected from ISOLDE) is a unique facility designed to produce unconventional radioisotopes with the right properties to enhance the precision of both patient imaging and treatment.
